Cell-type specific scATAC-seq profiles at a glance
Cell-type specific scATAC-seq profiles at a glance
Background: Heterogeneity and sparsity of scATAC-seq datasets
Single-cell Assay for Transposase Accessible Chromatin using sequencing (scATAC-seq) is a valuable resource to learn cis-regulatory elements such as cell-type specific enhancers and transcription factor binding sites. However, cell-type identification of scATAC-seq data is known to be challenging due to the heterogeneity derived from different protocols and the high dropout rate.Key idea: Meta-analytic marker genes for brain cell types
A key idea of our study is using meta-analytic marker genes, called SF marker set, derived from multiple scRNA-seq datasets from Brain Initiative Cell Census Network (BICCN). We developed a method, MetaMarkers, and used it to define a new meta-analytic marker gene set, which is the expanded marker set that includes co-expressed genes of marker genes. The gene set is made by selecting the top 100 genes to predict 85 cortical cell types accurately by their aggregated signals.Integrative server: Cell-type specific scATAC-seq profiles from six studies
The heterogeneity of scATAC-seq datasets causes the disparity in terms of the number of cells and clusters, suggesting cluster-level annotation is inadequate and not comparable. Instead, we predicted the cells whose aggregated module activity is ranked within the top 500 using SF marker gene sets. Then we produced the meta scATAC-seq profiles based on those cell-type annotation. In this server, the average read count of each genomic location can be visualized in a genome browser for certain cell types or datasets.Deep learning prediction: Sequence-dependent and -independent chromatin accessibility regulation
Furthermore, to assess the potential of genomic sequences to regulate the cell-type specific cis-regulatory programs, we integrated predicted chromatin accessibility data using a sequence-based deep CNN trained on the BICCN scATAC-seq data.Example
1. Cross dataset analysis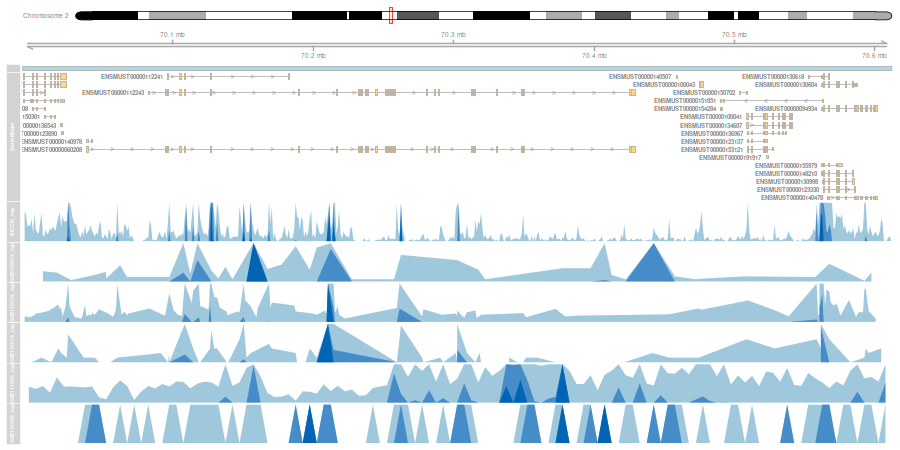
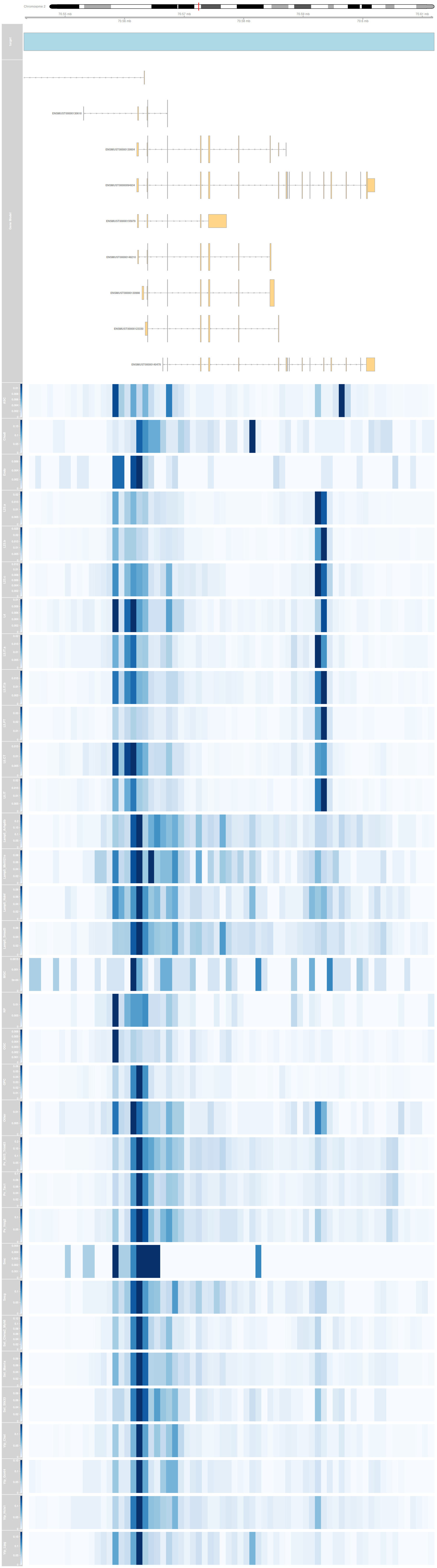
2. Cross cell-type analysis
Reference
- Kawaguchi RK, et al. Exploiting marker genes for robust classification and characterization of single-cell chromatin accessibility. bioRxiv (2021)
- BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network (BICCN): Yao, Z., et al. A transcriptomic and epigenomic cell atlas of the mouse primary motor cortex. Nature 598, 103–110 (2021)
- Preissl, S., et al. Single-nucleus analysis of accessible chromatin in developing mouse forebrain reveals cell-type-specific transcriptional regulation. Nature neuroscience, 21(3):432-439 2018.
- Cusanovich DA., et al. A Single-Cell Atlas of In Vivo Mammalian Chromatin Accessibility. Cell, 23;174(5):1309-1324.e18 2018.
- Lareau, CA., et al. Droplet-based combinatorial indexing for massive-scale single-cell chromatin accessibility. Nature Biotechnology 37(8):916-924 2019.
- Chen, S., et al. High-throughput sequencing of the transcriptome and chromatin accessibility in the same cell. Nature biotechnology, 37(12):1452-1457 2019.
- Zhu, C., et al. An ultra high-throughput method for single-cell joint analysis of open chromatin and transcriptome. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 2019.
- Spektor, R., et al. Single cell atac-seq identifies broad changes in neuronal abundance and chromatin accessibility in down syndrome. bioRxiv, 2019.
History
2022.05.31 First release.2021.10.21 New data released.
2021.10.18 Pre-release.
Cross dataset analysis for each cell type
Integrative annotation using meta-analytic marker genes
- Due to the limitation of technology and resource, there is a variation in the granularity of each scATAC-seq data granularity (9 to 36 clusters).
- The annotated cell types include major cell types and more detailed cell types, such as Pvalb or Vip within inhibitory neuronal cells.
- To overcome the heterogeneity of scATAC-seq datasets, we reannotated all scATAC-seq data for detailed cell types at each cell level rather than clusters.
- We compute module activity of meta-analytic marker gene sets to capture cell-type specific signal at single-cell level.
- The top 500 cells are extracted from each dataset according to the enrichment of module activity for each cell type to compute meta scATAC-seq profiles.
Loading...
Surrounding gene information
Cross cell-type analysis within each dataset
Cell-type specific meta profiles within each dataset
- Cluster-specific pseudo-bulk profiles are computed for each dataset.
- Moreover, predicted scATAC-seq profiles from DNA sequence only are shown as a representative of sequence-dependent chromatin accessibility.
- The model for prediction is trained for all clusters found in the BICCN datasets.
Loading...
Loading...
Overlapped genes
Reannotation of original clusters
Module activity of meta-analytic marker genes for clusters
Cell-type characterization of each cluster based on overlap of cluster-specific genes and marker gene set.
1. Major cell type: IN (inhibitory), EX (excitatory), and NN (non neuronal)
2' Neuronal subtype (IN) Lamp5, Pvalb, Sncg, Sst, and Vip
2'' Neuronal subtype (EX): L2.3 IT, L5.IT, L5.ET, L5.6.NP, L6.IT.Car3, L6.CT, L6.b
Other conditions - score: normalized Jaccard index, # of cluster-specific genes: 1000, # of marker genes: 100.
Loading...
Marker gene sets
Pseudo-bulk profiles of scATAC-seq data
Meta-analysis of scATAC-seq cell-type characterization
Learning single-cell chromatin accessibility profiles using meta-analytic marker genes Risa Karakida Kawaguchi, Ziqi Tang, Stephan Fischer, Chandana Rajesh, Rohit Tripathy, Peter K. Koo, Jesse Gillis. bioRxiv 2021.04.01.438068; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.01.438068
Deep learning model
Marker set construction
How many markers are needed to robustly determine a cell’s type? Stephan Fischer, Jesse Gillis. bioRxiv 2021.04.16.439807; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.16.439807